Generation IV Goals, Technologies and GIF R&D Roadmap
For over twenty years, the Generation IV International Forum (GIF) has supported global cooperative initiatives to develop advanced nuclear energy systems addressing future global energy requirements. The objectives set for Generation IV designs encompass enhanced fuel efficiency, minimized waste generation, economic competitiveness, and adherence to rigorous safety and proliferation resistance measures.
Initially, GIF conducted a comprehensive review of reactor technologies, eventually focusing on six promising technologies.
Subsequently, a research and development (R&D) roadmap was established and periodically refined, directing GIF and its member towards the realization of these Generation IV nuclear energy systems.
The Generation IV Goals
Eight technology goals have been defined for Generation IV systems in four broad areas: sustainability, economics, safety and reliability, and proliferation resistance and physical protection. These ambitious goals are shared by a large number of countries as they aim at responding to the economic, environmental and social requirements of the 21st century. They establish a framework and identify concrete targets for focusing GIF R&D efforts.
These goals guide the cooperative R&D efforts undertaken by GIF members. The challenges raised by GIF goals are intended to stimulate innovative R&D covering all technological aspects related to design and implementation of reactors, energy conversion systems, and fuel cycle facilities.
In light of the ambitious nature of the goals involved, international cooperation is considered essential for a timely progress in the development of Generation IV systems. This cooperation makes it possible to pursue multiple systems and technical options concurrently and to avoid any premature down selection due to the lack of adequate resources at the national level.
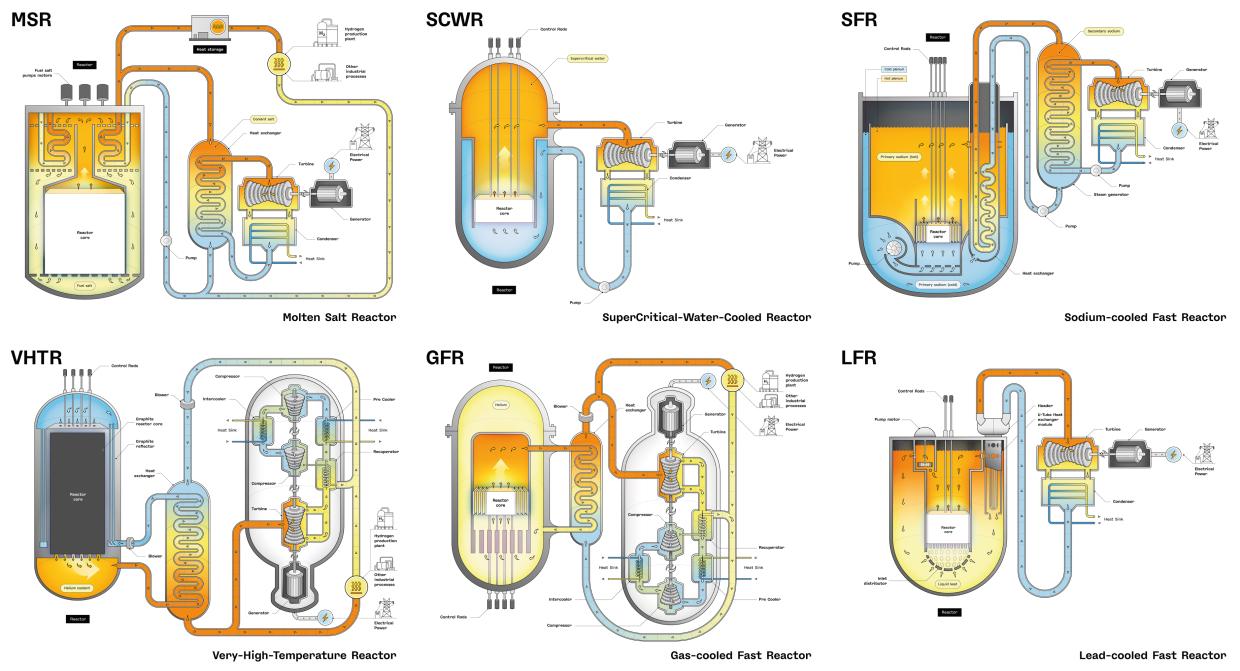
With these goals in mind, some 100 experts evaluated 130 reactor concepts before GIF selected six reactor technologies for further research and development. These include the: Gas-cooled Fast Reactor (GFR), Lead-cooled Fast Reactor (LFR), Molten Salt Reactor (MSR), Supercritical Water-cooled Reactor (SCWR), Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR) and Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR).
Some of these reactor designs could be demonstrated within the next decade, with commercial deployment beginning in 2030.
Generation IV Technology Systems
The goals adopted by GIF provided the basis for identifying and selecting six nuclear energy systems for further development. The selected systems rely on a variety of reactor, energy conversion and fuel cycle technologies. Their designs feature thermal and fast neutron spectra, closed and open fuel cycles as well as a wide range of reactor sizes from very small to very large. Depending on their respective degrees of technical maturity, the Generation IV systems are expected to become available for commercial introduction in the period around 2030 or beyond. The path from current nuclear systems to Generation IV systems is described in a 2002 roadmap report entitled A Technology Roadmap for Generation IV nuclear energy systems that was updated several times.
All Generation IV systems aim at performance improvement, new applications of nuclear energy, and/or more sustainable approaches to the management of nuclear materials. High-temperature systems offer the possibility of efficient process heat applications and eventually hydrogen production. Enhanced sustainability is achieved primarily through the adoption of a closed fuel cycle including the reprocessing and recycling of plutonium, uranium and minor actinides in fast reactors and also through high thermal efficiency. This approach provides a significant reduction in waste generation and uranium resource requirements. The table below summarises the main characteristics of the six Generation IV systems.
| Generation IV System | Neutron | Coolant | Outlet Temperature °C | Fuel | Size (MWe) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VHTR (Very-high-temperature reactor) | Thermal | Helium | 900-1000 | Open | 250-300 |
| SFR (Sodium-cooled fast reactor) | Fast | Sodium | 500-550 | Closed | 50-150 |
| SCWR (Supercritical-water-cooled reactor) | Thermal/fast | Water | 510-625 | Open/closed | 300-700 |
| GFR (Gas-cooled fast reactor) | Fast | Helium | 850 | Closed | 1 200 |
| LFR (Lead-cooled fast reactor) | Fast | Lead | 480-570 | Closed | 20-180 |
| MSR (Molten salt reactor) | Thermal/fast | Fluoride salts | 700-800 | Closed | 1000 |
The very-high-temperature reactor is a further step in the evolutionary development of high-temperature reactors. The VHTR is a helium-gas-cooled, graphite-moderated, thermal neutron spectrum reactor with a core outlet temperature higher than 900 C, and a goal of 1 000 C, sufficient to support high temperature processes such as production of hydrogen by thermo-chemical processes. The reference thermal power of the reactor is set at a level that allows passive decay heat removal, currently estimated to be about 600 MWth. The VHTR is useful for the cogeneration of electricity and hydrogen, as well as to other process heat applications. It is able to produce hydrogen from water by using thermo-chemical, electro-chemical or hybrid processes with reduced emission of CO2 gases. At first, a once-through LEU (<20% 235U) fuel cycle will be adopted, but a closed fuel cycle will be assessed, as well as potential symbiotic fuel cycles with other types of reactors (especially light-water reactors) for waste reduction purposes.
The sodium-cooled fast reactor system uses liquid sodium as the reactor coolant, allowing high power density with low coolant volume fraction. It features a closed fuel cycle for fuel breeding and/or actinide management. The reactor may be arranged in a pool layout or a compact loop layout. The reactor-size options which are under consideration range from small (50 to 150 MWe) modular reactors to larger reactors (300 to 1 500 MWe). The two primary fuel recycle technology options are advanced aqueous and pyrometallurgical processing. A variety of fuel options are being considered for the SFR, with mixed oxide preferred for advanced aqueous recycle and mixed metal alloy preferred for pyrometallurgical processing. There is a significant past experience accumulated with sodium cooled reactors in several countries, and reactors of this technology are currenlty operating and under development.
Supercritical-water-cooled reactors are a class of high-temperature, high-pressure water-cooled reactors operating with a direct energy conversion cycle and above the thermodynamic critical point of water (374°C, 22.1 MPa). The higher thermodynamic efficiency and plant simplification opportunities afforded by a high-temperature, single-phase coolant translate into improved economics. A wide variety of options are currently considered: both thermal-neutron and fast-neutron spectra are envisaged; and both pressure vessel and pressure tube configurations are considered.
The gas-cooled fast reactor combines the advantages of a fast neutron core and helium coolant giving possible access to high temperatures. It requires the development of robust refractory fuel elements and appropriate safety architecture. The use of dense fuel such as carbide or nitride provides good performance regarding plutonium breeding and minor actinide burning.
The lead-cooled fast reactor system is characterised by a fast-neutron spectrum and a closed fuel cycle with full actinide recycling, possibly in central or regional fuel cycle facilities. The coolant may be either lead (preferred option), or lead/bismuth eutectic. The LFR may be operated as a breeder, a burner of actinides from spent fuel, using inert matrix fuel, or a burner/breeder using thorium matrices. Two reactor size options are considered: a small 50-150 MWe transportable system with a very long core life, and a medium 300-600 MWe system. In the long term a large system of 1 200 MWe may be envisaged.
The molten-salt reactor system embodies the very special feature of a liquid fuel. MSR concepts, which may be used as efficient burners of transuranic elements from spent light-water reactor (LWR) fuel, also have a breeding capability in any kind of neutron spectrum ranging from thermal (with a thorium fuel cycle) to fast (with a uranium-plutonium fuel cycle). Whether configured for burning or breeding, MSRs have considerable promise for the minimisation of radiotoxic nuclear waste.
GIF Technology Roadmap and R&D Outlook
The technology roadmap defines and plans the necessary research and development (R&D) to support the next generation of innovative nuclear energy systems known as Generation IV. The roadmap represents a concerted international effort of ten countries; Argentina, Brazil, Canada, France, Japan, Republic of Korea, South Africa, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, the United States, in addition to, the International Atomic Energy Agency and the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency.
In 2001, over 100 experts from these countries and international organisations began work on defining the goals for new systems, identifying many promising concepts, evaluating them, and defining the R&D needed for the most promising systems*. By the end of 2002, the work resulted in a description of the six most promising systems and their associated R&D needs. The six systems feature increased safety, improved economics for electricity production and new products such as hydrogen for transportation applications, reduced nuclear wastes for disposal, and increased proliferation resistance.
In 2009, the Experts Group published the Generation IV R&D Outlook, to provide a view of what GIF members hope to achieve collectively in the period 2010-2014.
As part of the GIF Strategic Planning activity launched in 2012, the Technology Roadmap has been updated under the coordination of a dedicated Task Force. The updated Roadmap takes into account plans to accelerate the development of some technologies by deploying prototypes or demonstrators within the next decade. The report is the result of discussions between the Task Force, the Experts Group and the different Systems Steering Committees.